By: Rizwan Sheikh, Senior data analyst at BMT Scientific Marine Services
 The need for mooring integrity monitoring has of late come back under the spotlight, not least because the use of floating production systems in the offshore Oil and Gas industry has been predicted to grow at a significant rate between now and 2017 with a peak in the number of new builds expected to occur in 2016/2017. Recently, an updated industry guideline on mooring integrity has been issued by Oil & Gas UK with the support of operators, contractors and vendors. The guideline reinforces how mooring integrity management through effective monitoring and data management can provide information to help detect mooring line failure and assist with validation of mooring design strength and fatigue analyses.
The need for mooring integrity monitoring has of late come back under the spotlight, not least because the use of floating production systems in the offshore Oil and Gas industry has been predicted to grow at a significant rate between now and 2017 with a peak in the number of new builds expected to occur in 2016/2017. Recently, an updated industry guideline on mooring integrity has been issued by Oil & Gas UK with the support of operators, contractors and vendors. The guideline reinforces how mooring integrity management through effective monitoring and data management can provide information to help detect mooring line failure and assist with validation of mooring design strength and fatigue analyses.
Station keeping through the life of a field is of critical importance for floating production facilities in all parts of the world. The mooring system performs this function, and although it has not always been the case, current design practice is to engineer mooring systems that can withstand extreme environments with single or even multiple line failure scenarios. Even so, the offshore industry has experienced numerous unexpected mooring line failures in recent years that, in a small number of cases, have resulted in mooring system failure. On average between 2001 and 2011, there were more than two mooring system failures per year. During this period, nine were multiple line failures1 and other mooring incidents resulted in riser failures and hence extended field shut down2. Based solely on these statistics, there is a clear business case for effective mooring integrity monitoring.
One of the challenges that has emerged from these failings is the need to monitor mooring system integrity reliably for the life of the facility without the need for costly inspection or maintenance of subsea sensors. In general, most mooring line monitoring systems that have been deployed to monitor mooring line tension have themselves experienced sensors failures, and the industry is now assessing ways of monitoring mooring line break detection as opposed to measuring mooring tension in a hope that the sensors will be more robust. However, many of the challenges of installing and maintaining these types of monitoring systems still need to be addressed.
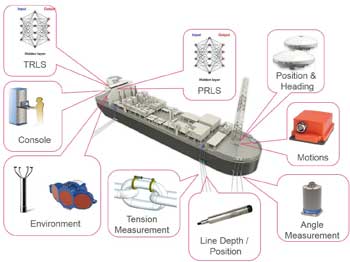
Typical requirements for mooring integrity monitoring of permanently moored floating systems encompass the need to measure mooring line tension and/or behavior, and to transmit this data to the facilities topside for display and archiving. Monitoring systems therefore need to be conceived to withstand high structural loads as well as harsh sea-states for the design life of the facility. This is achieved through robust design, proper installation and periodic maintenance and servicing once in service. Key questions to ask when selecting a system include: is the system for a new-build or a retrofit? Is position or inclination sufficient, or is a measurement of in-line tension required? Can the system be diver or ROV deployable or serviceable? Will data be transmitted wirelessly or through a hardwired connection? Last but not least, where is the most practical location to place the sensors without compromising safety or the quality of the measurement?
To meet the growing demand for a cost effective and reliable means of monitoring mooring system integrity, BMT has developed a novel system to assimilate data from a range of topside-based sensors (which monitor factors like the environment, position, vessel motions, draft and available mooring line information) into a topside Response Learning System (RLS). This system uses machine learning and cognitive science to learn the response of a system as well as the inter-dependencies of the numerous data sources. As a result, it is possible to estimate the behavior of a system (floating production facility) given a set of impulses (environmental loads from combined action of wind, wave and current) provided the RLS has sufficient measured marine data for learning.
There are numerous applications for machine learning algorithms. In fact, BMT is using them in the field to improve predictions of tension beneath the buoyancy can on a free-standing hybrid riser tower. In the context of mooring monitoring, work conducted on a turret moored FPSO, where a mooring line monitoring system was installed by BMT, showed that an RLS can estimate mooring line tension to within 30kN using only position and draft as inputs.
Excursion monitoring can also be used as an indirect way to monitor the integrity of the mooring system. Simple watch circle monitoring systems do not integrate metocean and vessel motions data to verify that the vessel offset from its moored origin is as should be expected, given the environmental loading and mooring stiffness. Furthermore, should the offset from design origin shift slightly in benign conditions, a watch circle processor would not be able to indicate a change in the mooring system. By using an RLS, the expected position, heading and response can be compared back to the measured position for the given environment. If the difference exceeds a pre-determined threshold, an advisory can be issued on the mooring system integrity.
In conclusion, with mooring integrity now under a renewed emphasis within the Oil & Gas industry, there is a heightened need for a robust and cost effective mooring integrity monitoring solution for both new-build and existing installations. The application of an RLS to monitor mooring system integrity builds upon BMT’s many years of experience in providing custom designed and custom built Integrated Marine and Mooring Line Monitoring Systems to the deepwater offshore oil and gas industry. With the rapid advances in computing power and data telemetry, the development of a topside based mooring integrity monitoring system like that described above is a natural progression and further unlocks the inherent value of data acquired by real-time monitoring systems.
http://www.bmt.be/en
Sources:
1 K. Ma, A. Duggal, P. Smedley, D. L’Hostis, H. Shu. “A Historical Review on Integrity Issues of Permanent Mooring Systems.” OTC 2013-24025, 2013.
2 S. Majhi, R. D’Souza. “Application of Lessons Learned from Field Experience to Design, Installation and Maintenance of FPS Moorings.” OTC 2013-24181, 2013.



 The need for mooring integrity monitoring has of late come back under the spotlight, not least because the use of floating production systems in the offshore Oil and Gas industry has been predicted to grow at a significant rate between now and 2017 with a peak in the number of new builds expected to occur in 2016/2017. Recently, an updated industry guideline on mooring integrity has been issued by Oil & Gas UK with the support of operators, contractors and vendors. The guideline reinforces how mooring integrity management through effective monitoring and data management can provide information to help detect mooring line failure and assist with validation of mooring design strength and fatigue analyses.
The need for mooring integrity monitoring has of late come back under the spotlight, not least because the use of floating production systems in the offshore Oil and Gas industry has been predicted to grow at a significant rate between now and 2017 with a peak in the number of new builds expected to occur in 2016/2017. Recently, an updated industry guideline on mooring integrity has been issued by Oil & Gas UK with the support of operators, contractors and vendors. The guideline reinforces how mooring integrity management through effective monitoring and data management can provide information to help detect mooring line failure and assist with validation of mooring design strength and fatigue analyses. International oilfield services company,
International oilfield services company, 
 Reducing expenditure while continuing to improve safety and reduce risk is a key driver for the oil and gas industry especially in today’s cost constrained environment.
Reducing expenditure while continuing to improve safety and reduce risk is a key driver for the oil and gas industry especially in today’s cost constrained environment. 
 Global inspection, repair and maintenance (IRM) company
Global inspection, repair and maintenance (IRM) company  International oilfield support services company
International oilfield support services company  NYC-based
NYC-based  McDermott deepwater rigid reel Lay Vessel 105 (LV 105) is slated to complete offshore installation in early 2016. (Photo: Business Wire)
McDermott deepwater rigid reel Lay Vessel 105 (LV 105) is slated to complete offshore installation in early 2016. (Photo: Business Wire)  The Extel Survey gathers the views and rankings of international research analysts for the world's largest publicly traded companies
The Extel Survey gathers the views and rankings of international research analysts for the world's largest publicly traded companies Blackford Dolphin
Blackford Dolphin
 Cutting through complexity
Cutting through complexity
 Leveraging its expertise to meet ultra-deepwater challenges
Leveraging its expertise to meet ultra-deepwater challenges