In response to the findings of investigations into the Deepwater Horizon tragedy, and following a thorough evaluation of recommendations from industry groups, equipment manufacturers, federal agencies, academia and environmental organizations, Secretary of the Interior Sally Jewell announced on Monday, proposed regulations to better protect human lives and the environment from oil spills. The measures include more stringent design requirements and operational procedures for critical well control equipment used in offshore oil and gas operations.
“Both industry and government have taken important strides to better protect human lives and the environment from oil spills, and these proposed measures are designed to further build on critical lessons learned from the Deepwater Horizon tragedy and to ensure that offshore operations are safe,” said Secretary Jewell, who recently discussed the Administration’s energy reform agenda in remarks at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. “This rule builds on enhanced industry standards for blowout preventers to comprehensively address well design, well control and overall drilling safety.”
The proposed rule, which will be open for public comments, addresses the range of systems and equipment related to well control operations. The measures are designed to improve equipment reliability, building upon enhanced industry standards for blowout preventers and blowout prevention technologies. The rule also includes reforms in well design, well control, casing, cementing, real-time well monitoring and subsea containment.
The well control measures would implement multiple recommendations from various investigations and reports of the Deepwater Horizon tragedy, including the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Regulation and Enforcement/U.S. Coast Guard Joint Investigation-Forensic Equipment Analysis (September 2011); National Academy of Engineering (May 2012); National Oil Spill Commission (January 2011); Ocean Energy Safety Advisory Committee; Government Accountability Office and others. Interior’s Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE) thoroughly analyzed the results of the investigations, including nearly 370 specific recommendations, and conducted extensive outreach to derive further enhancements from stakeholder input, academia, and industry best practices, standards and specifications.
The blowout preventer, an essential piece of safety equipment used in offshore drilling operations, was a point of failure in the Deepwater Horizon event, but several other barriers failed as well. The cascade of multiple failures resulted in the loss of well control, an explosion, fire and subsequent months-long spill. In connection with this rulemaking, BSEE worked with a wide array of stakeholders to comprehensively address well control measures and equipment.
“We worked to collect the best ideas on the prevention of well control incidents and blowouts to develop this proposed rule – including knowledge and skillsets from industry and equipment managers,” said Assistant Secretary for Land and Minerals Management Janice Schneider. “This rule proposes both prescriptive and performance-based standards that are based on this extensive engagement and analysis.”
In May 2012, BSEE’s offshore energy safety forum brought together federal policy makers, industry, academia, and others to discuss additional steps the Bureau and the industry could take to continue to improve the reliability and safety of blowout preventers. Following the forum, BSEE received significant input and specific recommendations from industry groups, operators, equipment manufacturers, and environmental organizations.
“In addition to more stringent design requirements, the proposed rule requires improved controls of all repair and maintenance activities through the lifecycle of the blowout preventer and other well control equipment,” said BSEE Director Brian Salerno. “It would provide verification of the performance of equipment designs through third party verification, enhanced oversight of operations through real-time monitoring viewed onshore, and require operators to, during operations, utilize recognized engineering best standards that reduce risk.”
Today’s announcement is another step in the most ambitious reform agenda in the Department’s history to strengthen, update and modernize offshore energy regulations. Interior has made sweeping reforms for safe and responsible development, overhauling federal oversight by restructuring to provide independent regulatory agencies that have clear missions and are better-resourced to carry out their work, while keeping pace with a rapidly evolving industry. In the wake of the Deepwater Horizon blowout, explosion, and oil spill, BSEE strengthened preparedness and planning regulations applicable to oil and gas companies operating offshore, and raised the bar through new requirements for well design, production systems, blowout prevention, and well control equipment.
The Outer Continental Shelf is a critical component of our nation’s energy portfolio, accounting for more than 16 percent of the Nation’s oil production and about five percent of domestic natural gas production – bringing in revenues of over $7.4 billion dollars to the U.S. Treasury in 2014. There are more floating deepwater drilling rigs working in the Gulf of Mexico today than prior to the Deepwater Horizon spill, and drilling activity is expected to steadily increase over the coming year.
The public may submit comments on the proposed regulations during the 60-day comment period that begins April 15, 2015, when the proposed rule is published in the Federal Register. Comments may be submitted via regulations.gov, the federal government's official rulemaking portal. The proposed regulations are available here.


 Amid low oil prices, pressure is growing to find industry wide solutions which can reduce costs. The documentation demanded today for subsea operations is time-consuming, complex and costly to deliver. Now a
Amid low oil prices, pressure is growing to find industry wide solutions which can reduce costs. The documentation demanded today for subsea operations is time-consuming, complex and costly to deliver. Now a  Steel forgings are important building blocks for subsea components and are often tailored to meet end-users’ specific requirements. This results in long delivery times and repeated follow-ups throughout the supply chain. With DNV GL’s new Recommended Practice (RP) ’Steel forgings for subsea applications’ these requirements are now harmonized. The implementation of the RP will enable reduced lead times, enhanced stock keeping, interchangeability of forgings and help to improve and maintain consistent quality.
Steel forgings are important building blocks for subsea components and are often tailored to meet end-users’ specific requirements. This results in long delivery times and repeated follow-ups throughout the supply chain. With DNV GL’s new Recommended Practice (RP) ’Steel forgings for subsea applications’ these requirements are now harmonized. The implementation of the RP will enable reduced lead times, enhanced stock keeping, interchangeability of forgings and help to improve and maintain consistent quality. Operator
Operator 


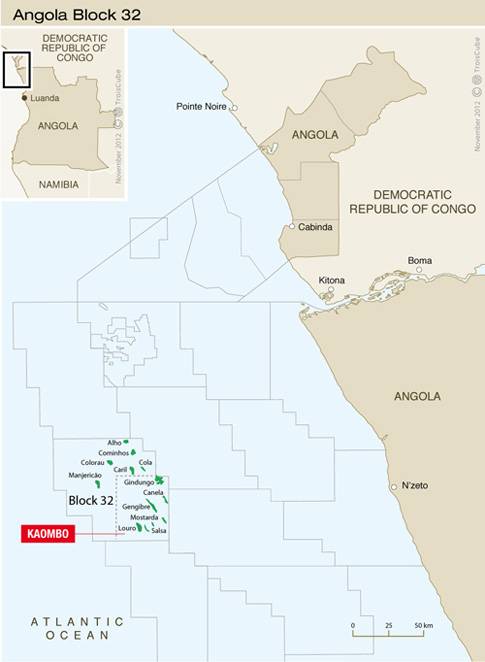 Total E & P Angola has awarded the marine warranty services (MWS) contract for their flagship Kaombo project. Angola is a country of strategic importance for
Total E & P Angola has awarded the marine warranty services (MWS) contract for their flagship Kaombo project. Angola is a country of strategic importance for  After thorough environmental analysis and substantial opportunity for public input, the Department of the Interior has issued a
After thorough environmental analysis and substantial opportunity for public input, the Department of the Interior has issued a 
 “Lessons still to be learned on fifth anniversary of Macondo”
“Lessons still to be learned on fifth anniversary of Macondo” 
 Early Wednesday morning the dehydration and pumping area caught fire in the Permanent Abkatun platform in the Bay of Campeche.
Early Wednesday morning the dehydration and pumping area caught fire in the Permanent Abkatun platform in the Bay of Campeche. ▪ U.S. could miss out on widely acknowledged economic and environmental benefits associated with LNG exports
▪ U.S. could miss out on widely acknowledged economic and environmental benefits associated with LNG exports